v2025-10-23 or later
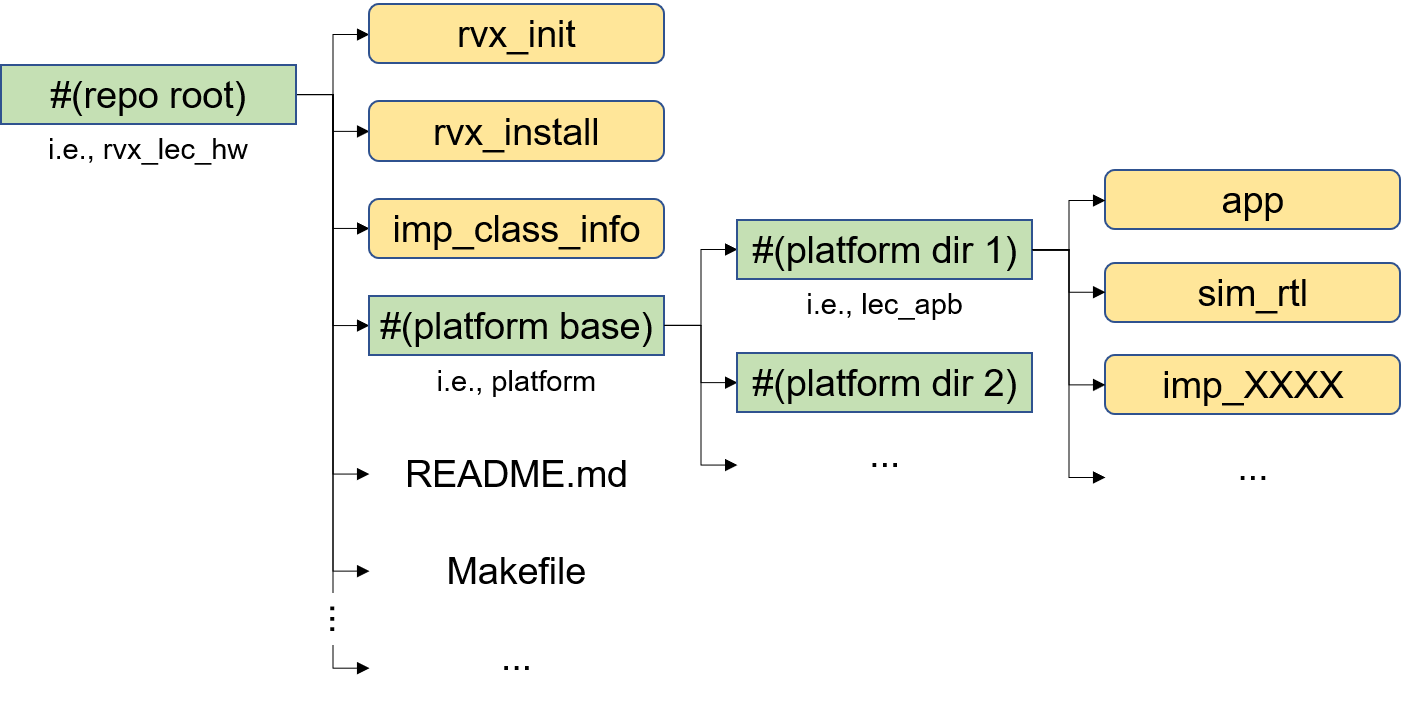
A platform includes both the hardware and software associated with an SoC. It is organized under a directory that shares the same name as the SoC the user intends to design.

In Figure 1, lec_apb is both the name of the SoC and the name of the corresponding directory.
The structure under #(platform dir) is as follows:
| Path | Usage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ./#(platform name).xml | Editable | SoC description file |
| ./app/ | Editable | Application development environment |
| ./user/ | Editable | User-managed environment |
| ./util/ | Editable | Utility environment |
| ./sim_rtl/ | Use Only | RTL simulation environment |
| ./imp_XXXX/ | Use Only | FPGA prototyping environment |
| ./arch/ | System Reserved | Generated from ./#(platform name).xml |
| ./fpga_component/ | System Reserved | Used in imp_XXXX |
Command:
cmd) cd #(platform base)
cmd) make new PLATFORM_NAME=#(platform name)Result:
#(platform base)/#(platform
name) is created,
which we refer to as #(platform dir).
Prerequisite: Creating a New Platform
Command:
cmd) cd #(platform dir)
inst) Edit the ./#(platform name).xml file with a text editor.Prerequisite: Designing a Platform
Command:
cmd) cd #(platform dir)
cmd) make synResult: #(platform dir)/arch is created.
Note: #(platform dir)/arch is automatically managed by the RVX tool.
The following files and/or directories are maintained:
./#(platform name).xml,
./app, ./user, and ./util
cmd) cd #(platform dir)
cmd) make clean